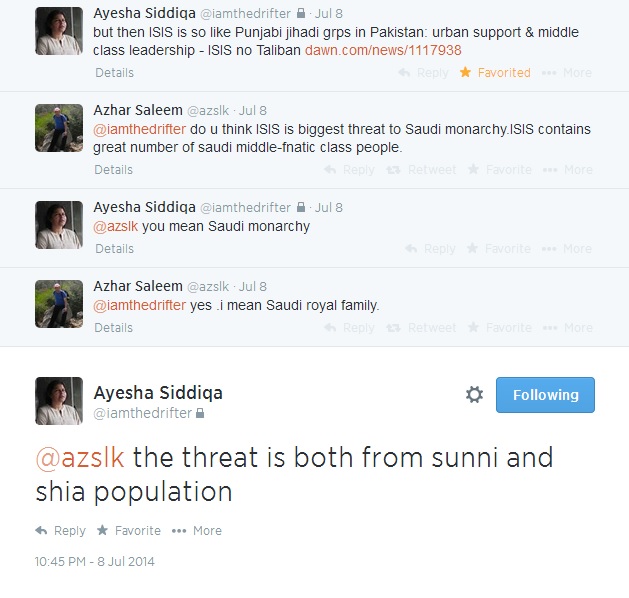
Analyst Zahid Hussain is completely off base: Dr. Ayesha Siddiqa says ISIS Al Qaeda & Deobandi Taliban are fruits of the same tree
Zahid Hussain goes to great lengths to show ISIS is very different from Punjabi Taliban Takfiri Deobandi Sipah e Sahaba or the TTP. Zahid Hussain is maligning Sunni Muslims by saying that the Takfiri Deobandi or Salafi (Wahhabi) doctrines are Sunni Islam.
Zahid Haussain ignores the Wahhabi and Deobandi terrorism conveyor belt is causing the destruction of the secular, tolerant state of Syria, and the Wahhabi and Deobandi Muslim desire to conquer the West. It may be noted that Saudi-funded Deobandi sect is semi-Wahhabi in its Jihadist and violent orientation and is responsible for majority of terrorist activities in Europe, South Asia and other regions. The conveyor belt, with the passage of time, will produce progressively worst or more puritanical Takfiri Salafis or Deoabandis.
In the same manner that Taliban who were funded and nurtured by Pakistan Army are now fighting the Pakistan Army and State, the groups funded by Saudis to promote Wahhabism will continue to spawn more radical and puritanical off shoots which will threaten the parent (Saudi Arabia) as well.
Zahid Hussain should also remember the Mujahideen that initially fought the Russains were not Takfiri. The next generation of Taliban and Al Qaeda were not Takfiri. The nature of Wahhbism is being the best (or worst) Muslim. So the conveyor will continually evolve a stricter and stricter version until everyone is a target.

THE dramatic rise of the Islamic State organisation formerly known as Islamic State of Iraq and Syria (ISIS) and its proclamation of a so-called caliphate portend a new and more brutal face of global jihadism. The organisation may not espouse Al Qaeda’s global agenda of terrorism; nevertheless, it is terribly wrong to compare the group with the Pakistani and Afghan Taliban.
ISIS is a phenomenon in itself with an ambition of extending its rule over the entire Muslim world. Representing a more radical version of Sunni Islam it seems to have already marginalised Al Qaeda at least in the Arabian peninsula. The stunning victories gained by ISIS, largely owing to its superior organisational capability, has helped the group take control of large parts of the region known as the cradle of civilisation.
Despite their fierce rivalry in the battle for Syria, ISIS and Al Qaeda are not ideologically very distinct from each other. The cadres of both militant networks are inspired by the same jihadist worldview. In fact, the group is an offshoot of Al Qaeda.
But both groups are unlike the Taliban whose support base is largely tribal and parochial. The ISIS fighters mostly come from urban educated backgrounds. The network has also drawn a sizeable number of young Muslim jihadists from the Western countries into its ranks. Some 3,000 foreigners form a large chunk of the group’s fighting force reflecting its global jihadist appeal.
The goal of ISIS is to extend its rule over the entire Muslim world.
Some analysts tend to draw a parallel between the rise of ISIS and that of the Taliban militia in Afghanistan in the 1990s. This argument cannot be more flawed. There is no similarity between the two groups at all.
For example, in his article titled ‘ISIS: the new Taliban’, published in the New York Review ofBooks, Ahmed Rashid argues: “In many ways, what the group is doing to Syria and Iraq resembles what the Taliban did in Afghanistan and Pakistan in the early 1990s.” He further contends that like the Taliban, ISIS’s war so far has been “about conquering territory rather than launching an Al Qaeda-style global jihad”.
While it may be true that the Taliban did not have a global jihad agenda and were only interested in establishing a retrogressive order in Afghanistan, that is certainly not correct in the case of ISIS. The group is truly committed to global jihad in contrast with the Afghan Taliban’s narrow local agenda. Though Mullah Omar had also declared himself ‘amirul momineen’ hisambitions have never been global. Unlike the Taliban supreme leader’s being a village mullah, the ISIS leader has a doctorate in Islamic ideology.
In a rare public appearance last week, ISIS leader Abu Bakar al Baghdadi (who has now declared himself ‘Caliph Ibrahim’) called for global jihad ordering the Muslims to ‘obey’ him. “I am the wali (leader) who presides over you,” declared Baghdadi.
Addressing the Friday congregation at the central mosque in Iraq’s second largest city of Mosul, which was recently captured by his fighters, Baghdadi admonished the Muslims: “Do jihad in the cause of God, incite the believers and be patient in the face of this hardship.” The changing of the group’s name is an expression of its ambitions beyond Iraq and Syria.
The purported ambition of ISIS is defined by a widely circulated online map showing the areas that the group ostensibly plans to bring under the control of the ‘caliphate’. They include most of the Muslim countries as well as parts of Europe that were once ruled by Muslims.
With its genesis deeply rooted in the sectarian conflict in Syria and Iraq, the organisation is essentially fighting an anti-Shia war. The killing of members of rival sects and the destruction of shrines is the hallmark of the group’s ideology. Though the Afghan and Pakistani Taliban too have a strong anti-Shia bias, that has not been the ideological base of their struggle.
A major factor contributing to the stunning success of ISIS is the vacuum created in Iraq and Syria by the collapsing state authority. The militant group has also benefited from the growing discontent among the minority Sunni community against the Shia-dominated government in Baghdad. In fact, the alliance with rebel Sunni tribes has played a critical role in the capture of northern Iraq by ISIS.
Notwithstanding its growing influence, ISIS remains a loosely connected sectarian group. The fact is that it is not such a single-minded monolith, but a coalition of radical Sunnis, former Baathist military officers and various tribal factions discontented with the government of Nouri al-Maliki.
Interestingly, while the militant organisation wants the people living in the regions under its control to observe ultra conservative Islamic traditions, it relies hugely on a hyper modern and sophisticated social media and even well-made feature-length movies to promote its ideology, recruit fighters and intimidate rival groups.
According to some analysts, the militant group has one of the most sophisticated social media strategies of any extremist group. Its powerful propaganda machine played an extremely important role in winning the psychological war against the enemy.
All that makes ISIS distinctly different from the rustic Pakistani and Afghan Taliban movements. The context of their respective wars also varies significantly. Although Pakistani and Afghan Taliban share the same retrogressive ideological worldview, even these two groups have some divergences. What is common among all three groups, however, is the use of terrorism as a major weapon to achieve their objectives.
The sectarian agenda of ISIS has already triggered the process of fragmentation of Iraq, which was unthinkable a few years ago. So the dream of uniting the Muslim world under a ‘caliphate’ is nothing more than a wild fantasy. What is most worrisome, however, is the creation of a new generation of global jihadists. There is genuine concern that thousands among the foreign militants fighting in Iraq and Syria may trigger a new wave of terrorism when they return to their home countries.
The writer is an author and journalist.
Twitter: @hidhussain